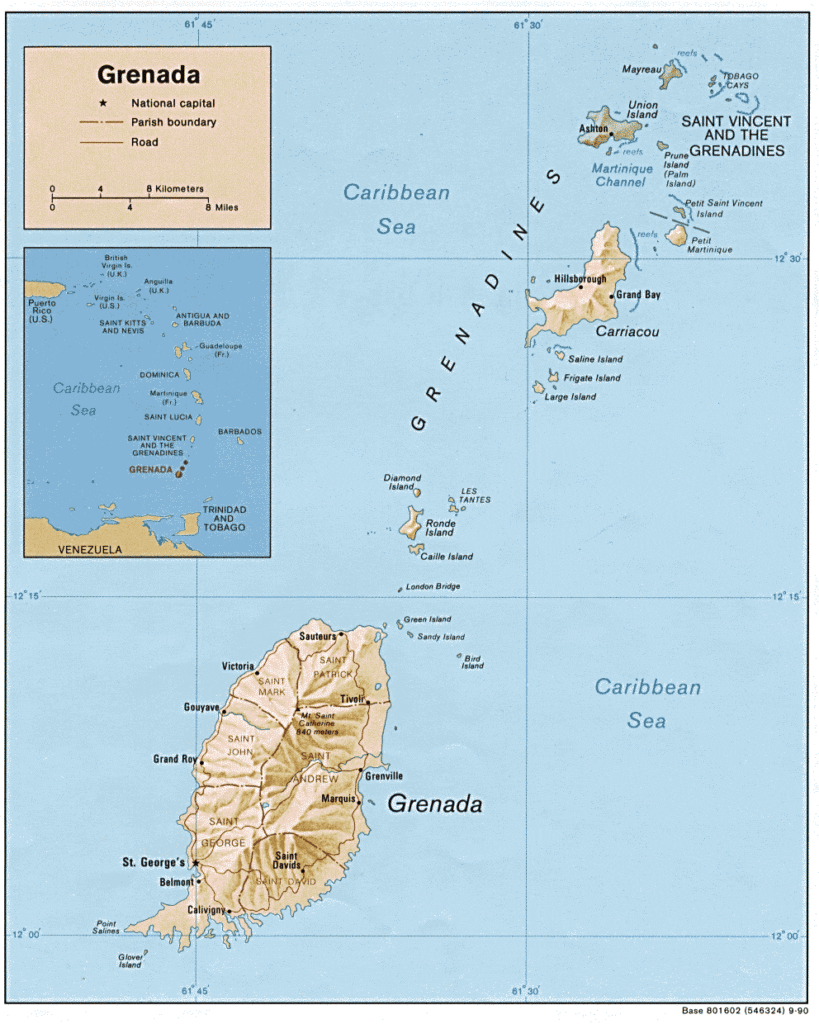
Grenada
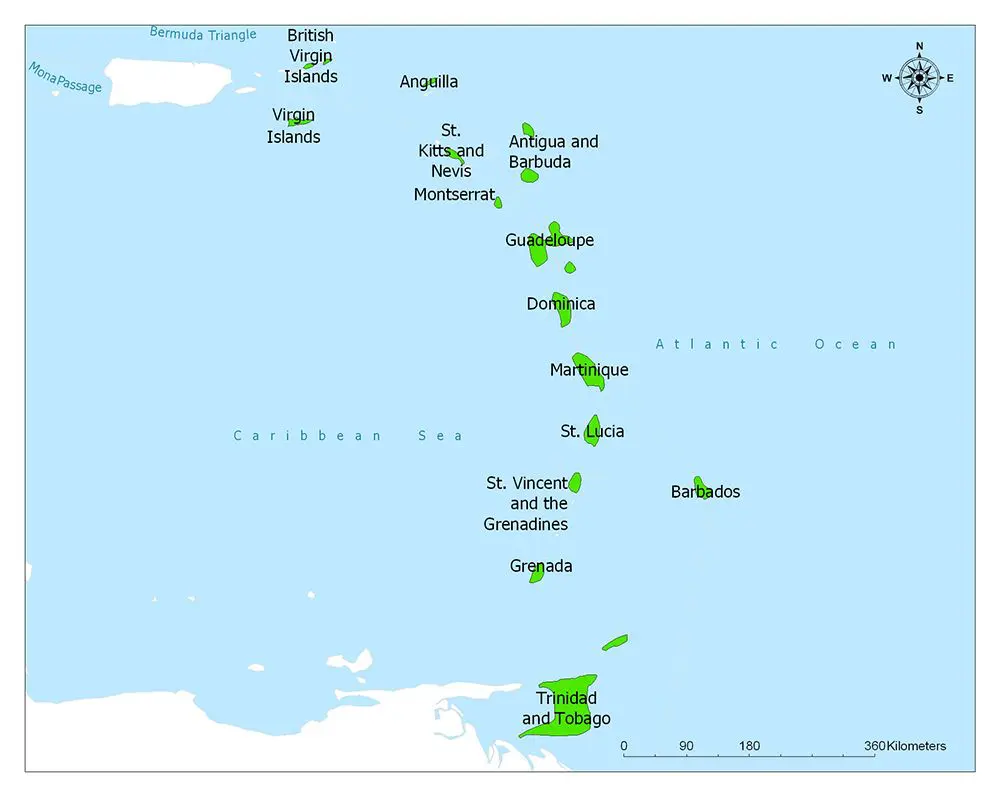
The Lesser Antilles, a long arc of small islands in the Caribbean Sea extending in a north-south direction from the Virgin Islands to Grenada. A number of other islands—Trinidad and Tobago, off the northeastern coast of Venezuela, and the east-west island chain from Margarita Island to Aruba, off the northern coast of Venezuela—are physiographically part of the South American continental shelf but are usually included in definitions of the Lesser Antilles.
Grenada is an island located between the Caribbean Sea and the Atlantic Ocean, north of Trinidad and Tobago. It is located at 12°07′N 61°40′W. It is the southernmost island of the Lesser Antilles. It is the southernmost island of the north-south arc of the Lesser Antilles.
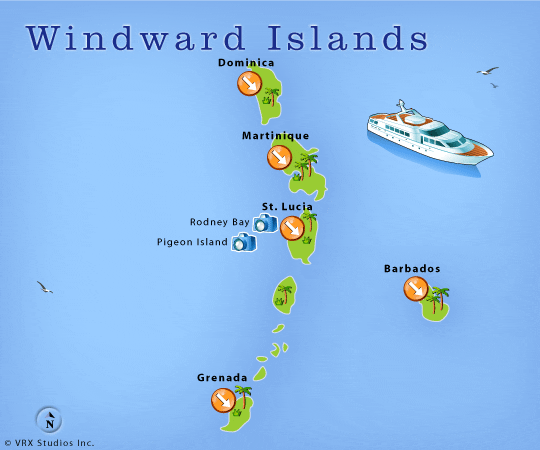
The Windward Islands, between latitudes 12° and 16° N and longitudes 60° and 62° W and include, from north to south, the English-speaking island of Dominica; the French département of Martinique; the English-speaking islands of Saint Lucia, Saint Vincent, and Grenada; and, between Saint Vincent and Grenada, the chain of small islands known as the Grenadines.

